Advancing Health Literacy in Clinical Research: Clear Communications for Every Participant

Introduction
One-third of the US population has health literacy levels that are basic or below basic [1]. This statistic, while surprising, is not unique to the United States: limited health literacy impacts access to appropriate health-related services around the world. The European Health Literacy Survey, for example, found that 12 percent of all respondents have inadequate general health literacy and 35 percent have problematic health literacy [2]. These numbers are likely higher in the clinical research context, given the complexity of clinical research information and the types of environments in which research conversations typically occur.
Clinical trials are an integral part of the practice of medicine and the delivery of health care. Clinical trials, and other clinical research, form the evidence base for many available treatment options and help determine whether the benefits of a new investigational treatment outweigh the potential risks. Further, comparative effectiveness research studies refine which existing clinical and public health interventions work best for improving health. The ethical design and conduct of all research involving human participants and their data rests on the premise that the participant understands and gives informed consent. Since consent and clinical trial participation are processes during which participants must be actively engaged, the development of clear and understandable materials to share with participants throughout their clinical research experience is crucial to successful study participation.
Supporting participant engagement in, and comprehension of, the clinical research process has become a central focus both within the United States and beyond. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) draft guidance assembled in response to the 21st Century Cures Act, entitled “Patient-Focused Drug Development: Collecting Comprehensive and Representative Input,” provides information on how stakeholders can collect and submit relevant experience and other data from patients and caregivers for medical product development and regulatory decision making [3]. In addition, the Revised Common Rule of the US Department of Health and Human Services requires that the informed consent form include a “concise and focused presentation of the key information that is most likely to assist a prospective subject or legally authorized representative in understanding the reasons why one might or might not want to participate in research” [4].
Further, recent regulations in Europe have mandated that reports containing end-of-study results be provided to research participants (after the regulatory effective date) [5]. Similar considerations within the United States are underway, as a draft guidance on the provision of plain language summaries of clinical trial results was submitted to the FDA in 2017 [6]. Some resources to support informed consent or other stages of clinical research already exist (for example, the US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s Informed Consent and Authorization Toolkit) [7]. Nevertheless, there was a need for an integrated and systems-based approach for providing clear and understandable clinical research information to research participants throughout the clinical trial.
Taking Action – Creating Resources for Clear Communications
In April 2018, the Multi-Regional Clinical Trials Center of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard (MRCT Center) convened a workgroup of diverse stakeholders—including patients and representatives from industry, academia, foundations, patient advocacy groups, nonprofit organizations, and government entities—to examine the issue of health literacy in clinical research. Over 18 months, the workgroup identified the challenges that low health literacy presents within the clinical research environment. In response, the workgroup developed and curated content to harness the opportunities that two-way communication can have when integrated throughout the entire clinical research life cycle.
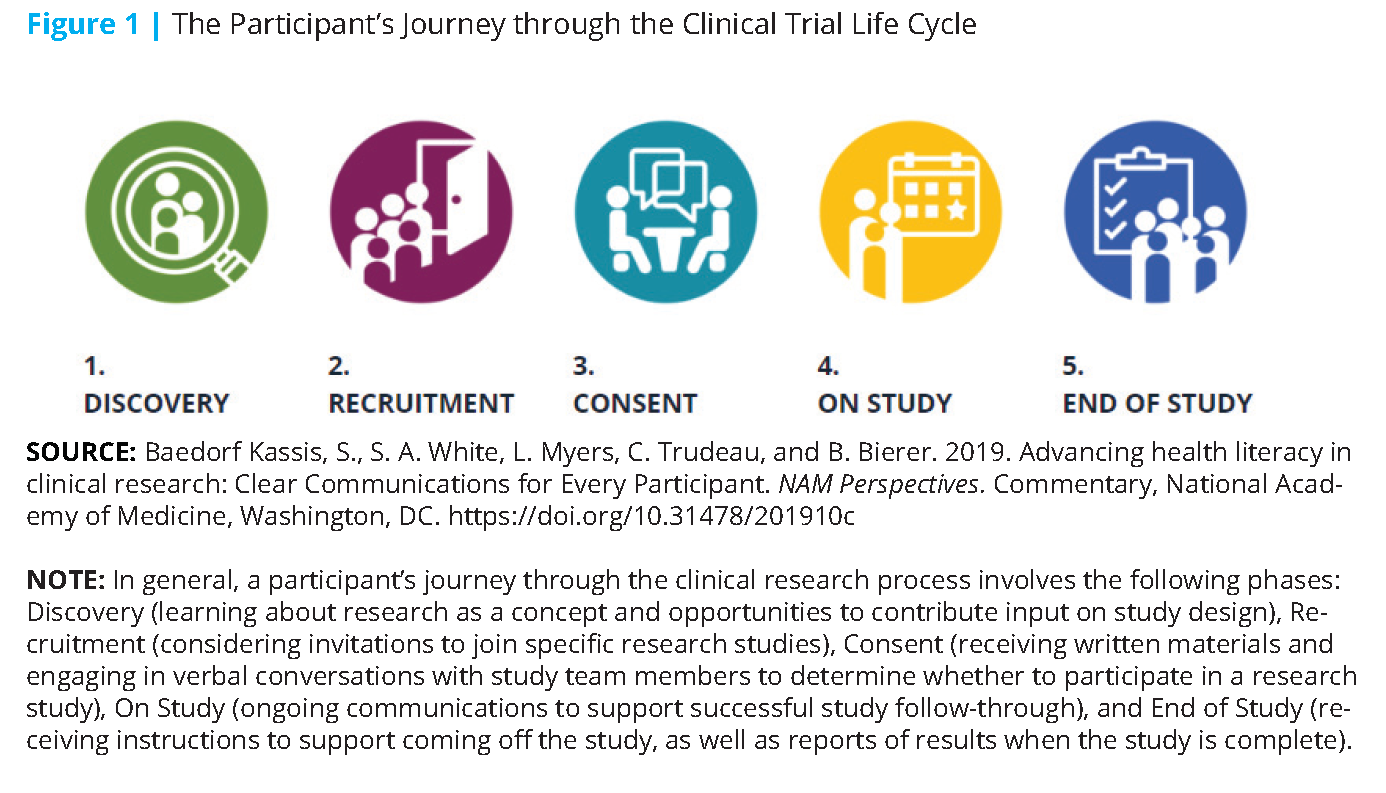
This content took the form of a suite of web-based resources that focus on five discrete stages of a participant’s clinical trial journey (i.e., Discovery, Recruitment, Consent, On Study, and End of Study, see Figure 1). The content includes resources to help identify the potential health literacy opportunities in each stage. For example, at the research “Discovery” stage, broad and early outreach to communities using health literacy best practices can increase their awareness of clinical research and how their population may benefit from these studies (see Figure 2). Further, at the “Discovery” stage, researchers can integrate the patient voice into the design and development of a study question. During the “On Study” stage, participants can also be provided with carefully designed study medication instructions to facilitate compliance with the study procedures and minimize attrition. All such efforts help build trust in the clinical research enterprise and can support future study-specific recruitment.
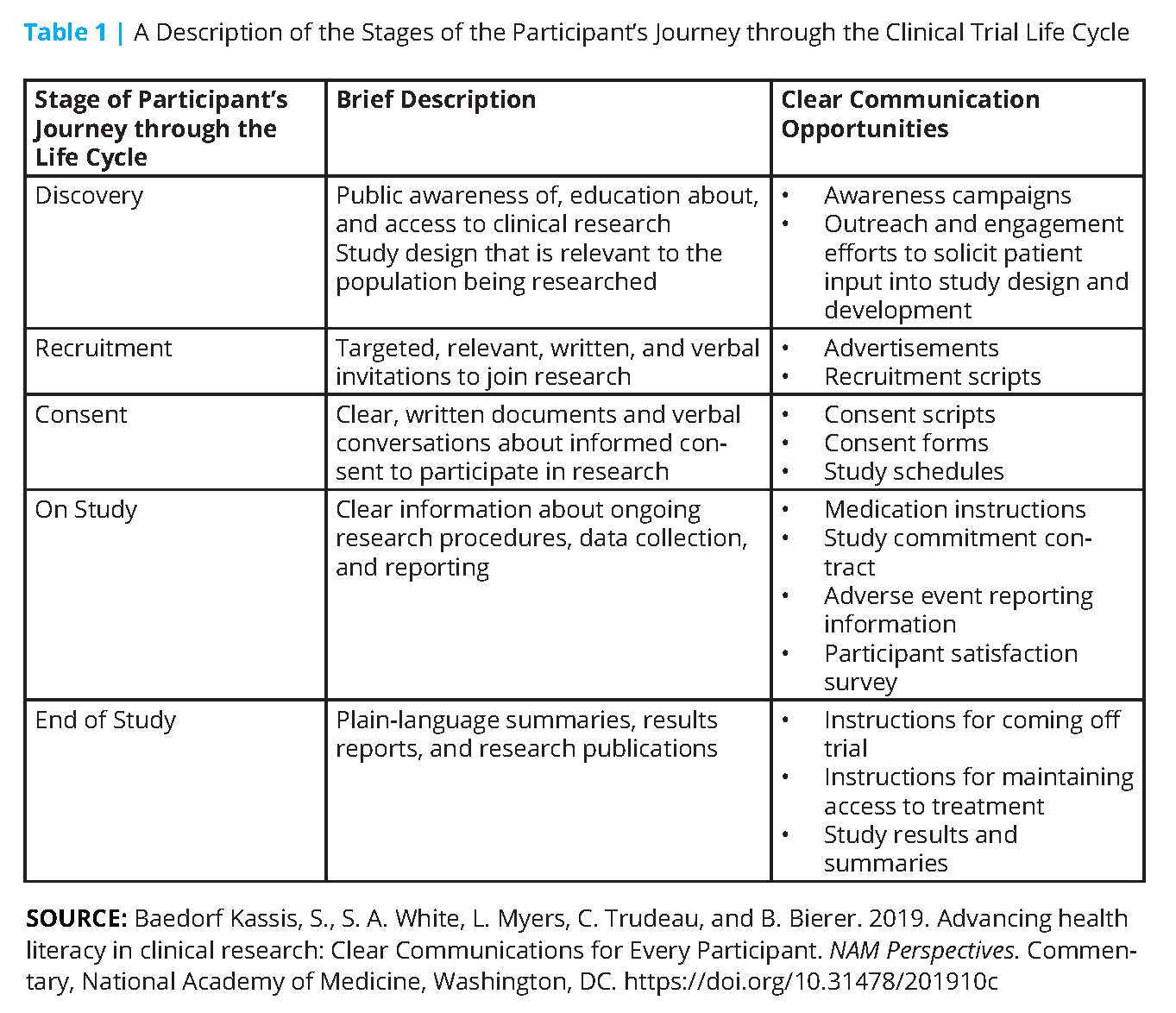
The workgroup designed targeted resources to help primary writers and reviewers of participant-facing materials, including funders, sponsors, investigators and their study teams, institutional review board members, and ethics committees. See Table 1 for additional examples.
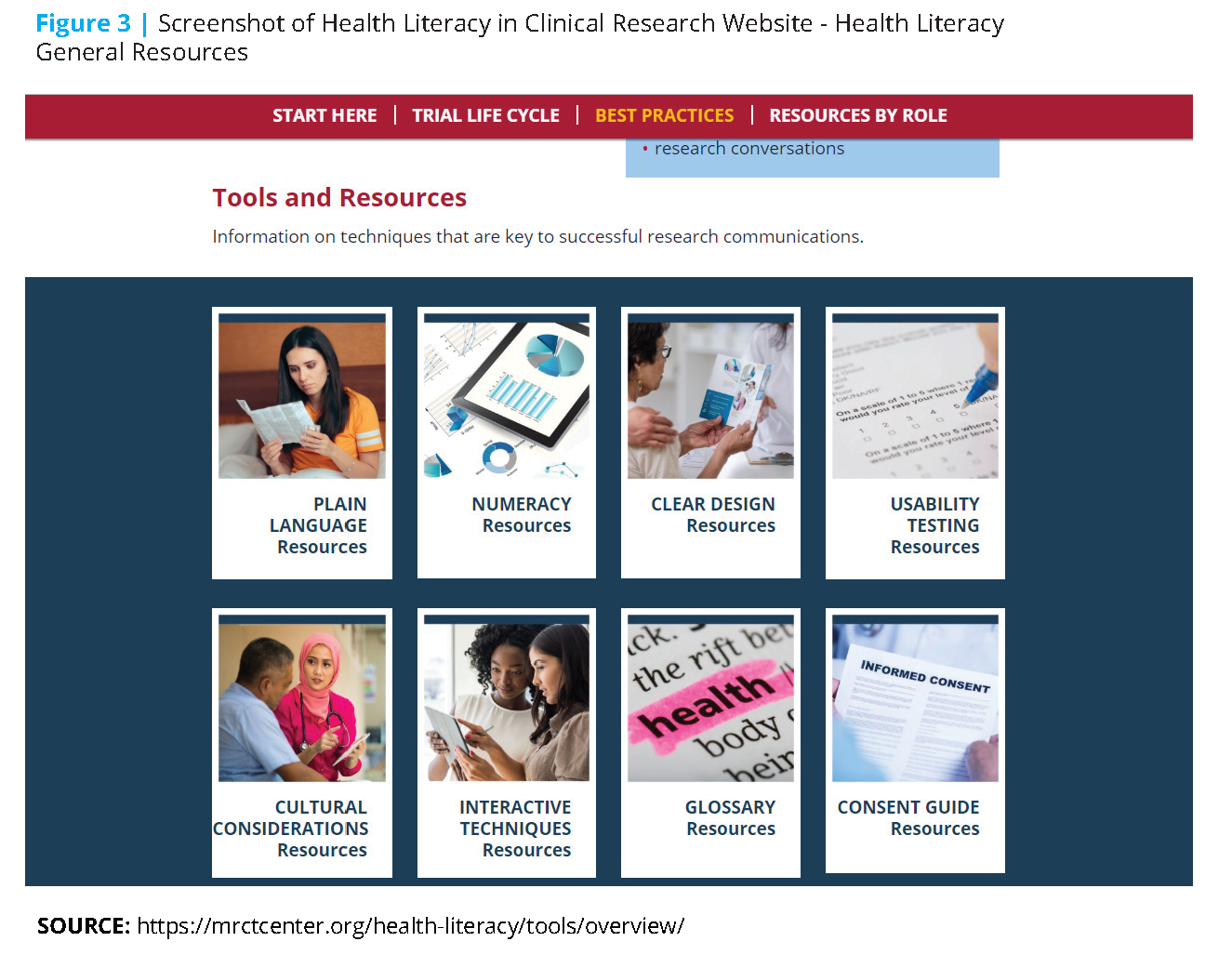
Underpinning all of the workgroup’s efforts is a broad definition of “health literacy” that extends beyond the widely cited individualistic definition (“a person’s ability to obtain, process, and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions)”[8]. Instead, the workgroup’s definition of “health literacy”, around which the Health Literacy in Clinical Research website (www.mrctcenter.org/ health-literacy) was designed, reflects the philosophy of a two-sided approach to health literacy and the need to expand the focus from participant understanding alone to the ability of communicators to present research information that is clear and understandable to the intended audience of potential, enrolled, and past trial participants. This broad definition encompasses principles of plain language, numeracy, and clear design, as well as other components deemed essential to effective communications, including cultural considerations, usability testing of materials, and supportive verbal interactions (see Figure 3). Creating clear communications that integrate health literacy best practices
involves more than simply writing at a sixth- to eighth- grade reading level; it involves integrating the feedback of the intended audience, considering their information and usability needs, and meeting those needs through tailored messaging.
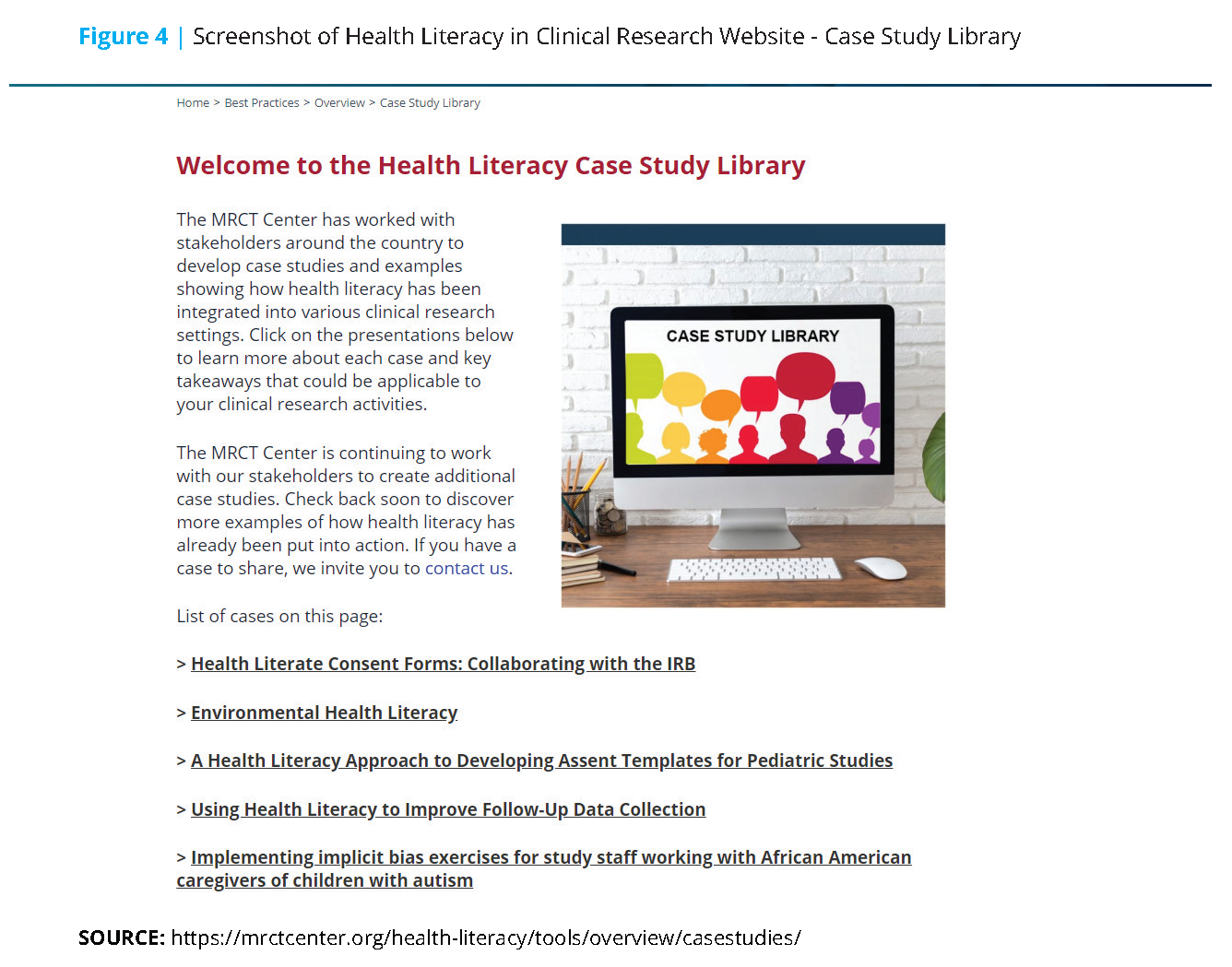
Health Literacy in Clinical Research principles were developed by the workgroup to form the foundation upon which all website content was built, and they encourage individual and organizational change. Additional highlights from the workgroup’s suite of digital materials include background information on health literacy, practical ways to integrate health literacy best practices into written and oral communications throughout the clinical trial life cycle, and overarching considerations for implementation. Further, the workgroup developed a case study library containing proof of concept scenarios that include informative examples of health literacy implementation such as an academic center’s development of health literate consent templates, the process by which one pharmaceutical company created health literate pediatric assent forms, a study team’s effort to address implicit bias, improvement of follow-up data collection, and sharing study findings with participants (see Figure 4).
The workgroup focused on the inclusion of the patient and participant voice throughout the clinical trial life cycle, conducting usability testing of participant materials, and adapting communications to the needs of the community. Of note, the entire website underwent a health literacy review, as well as tailored usability sessions with individuals representing industry, academia, institutional review boards and ethics committees, and patients who tested the website.
Conclusion
Clinical research stakeholders who develop, review, and approve participant-facing study materials should integrate health literacy best practices throughout the clinical trial life cycle and across different professional roles. By raising awareness, supporting advocacy, and bringing together clinical research–focused health literacy information in one place, the website resources highlighted above can help all stakeholders create clear, understandable communications that support research participants throughout their clinical trial journey. The work does not stop here. Additional tailored resources to support health literacy in clinical research will be added over time. In the near future, additional stakeholder-specific resources, including those tailored for participants will be developed. Sections of the Health Literacy in Clinical Research website will be further enhanced, including considerations of health literacy needs in other countries and materials for language translation. Working together, clinical research stakeholders can advance the systematic integration of health literacy best practices into all phases of clinical research.
Join the conversation!
![]() Tweet this! The authors of this #NAMPerspectives commentary created a toolkit to provide clear and understandable clinical research information to research participants throughout clinical trials. Read about it here: https://doi.org/10.31478/201910c #HealthLiteracyMonth @MRCTCenter
Tweet this! The authors of this #NAMPerspectives commentary created a toolkit to provide clear and understandable clinical research information to research participants throughout clinical trials. Read about it here: https://doi.org/10.31478/201910c #HealthLiteracyMonth @MRCTCenter
![]() Tweet this! Clinical trials are an integral part of the practice of medicine. The resources detailed in this #NAMPerspectives can help stakeholders create clear communications that support research participants. Read more: https://doi.org/10.31478/201910c #HealthLiteracyMonth @MRCTCenter
Tweet this! Clinical trials are an integral part of the practice of medicine. The resources detailed in this #NAMPerspectives can help stakeholders create clear communications that support research participants. Read more: https://doi.org/10.31478/201910c #HealthLiteracyMonth @MRCTCenter
![]() Tweet this! Those invested in clinical research should work to promote health literacy best practices into all phases of research. Learn more about mechanisms for better communication with these participants: https://doi.org/10.31478/201910c #NAMPerspectives #HealthLiteracyMonth @MRCTCenter
Tweet this! Those invested in clinical research should work to promote health literacy best practices into all phases of research. Learn more about mechanisms for better communication with these participants: https://doi.org/10.31478/201910c #NAMPerspectives #HealthLiteracyMonth @MRCTCenter
Download the graphics below and share them on social media!



References
- Crane Cutilli, C., and I. M. Bennett. 2010. Understanding the health literacy of America: Results of the National Assessment of Adult Literacy. Orthopaedic Nursing 28(1):27-34. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2668931 (accessed September 2, 2020).
- Kickbusch, I., J. M. Pelikan, F. Apfel, and A. D. Tsouros. 2013. Health literacy: The solid facts. Copenhagen, Denmark: WHO Regional Office for Europe. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/128703/e96854.pdf (accessed September 2, 2020).
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research and Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. 2018. Patient-focused drug development: Collecting comprehensive and representative input: Guidance for industry, Food and Drug Administration staff , and other stakeholders. Washington, DC: Food and Drug Administration. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/media/113653/download (accessed September 2, 2020).
- Electronic Code of Federal Regulations. N.d. Title 45, subtitle A, subchapter A, part 46. Available at: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/retrieveECFR?gp=&SID=83cd09e1c0f5c6937cd9d7513160fc3f&pitd=20180719&n=pt45.1.46&r=PART&ty=HTML (accessed October 24, 2019).
- European Commission. N.d. Clinical trials — Regulation EU no. 536/2014. Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/health/human-use/clinical-trials/regulation_en (accessed October 24, 2019).
- Regulations.gov. 2017. MRCT draft FDA guidance return of aggregate results. Available at: https://www.regulations.gov/document?D=FDA-2017-D-5478-0001 (accessed October 24, 2019).
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2019. Informed consent and authorization toolkit. Available at: https://www.ahrq.gov/funding/policies/informedconsent/index.html (accessed October 24, 2019).
- Ratzan, S. C., and R. M. Parker. 2000. Introduction. In National Library of Medicine current bibliographies in medicine: Health literacy, NLM Pub. No. CBM 2000-1, edited by C. R. Selden, M. Zorn, S. C. Ratzan, and R. M. Parker. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK216033 (accessed October 24, 2019).
- Brach, C., D. Keller, L. M. Hernandez, C. Baur, R. Parker, B. Dreyer, P. Schyve, A. J. Lemerise, D. Schillinger. 2012. Ten Attributes of Health Literate Health Care Organizations. NAM Perspectives. Discussion Paper, National Academy of Medicine, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.31478/201206a